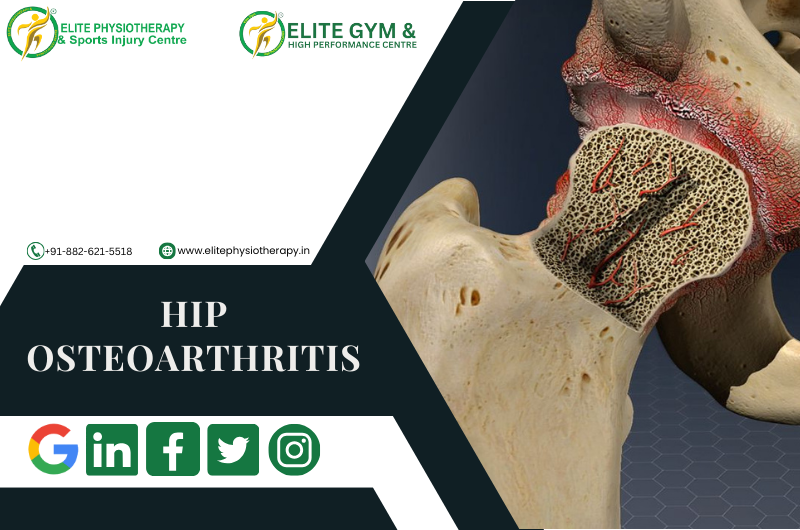
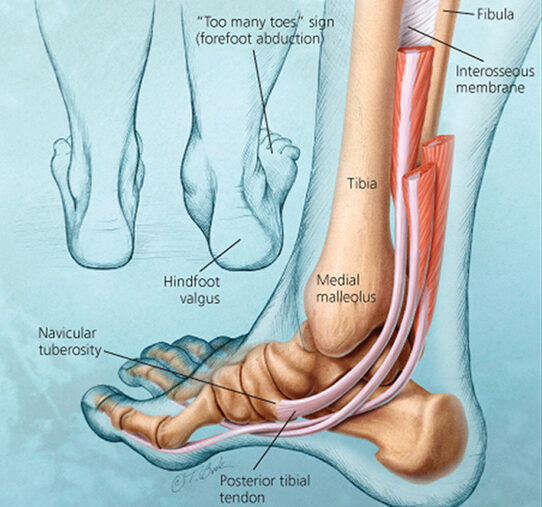
What is Hip Osteoarthritis?
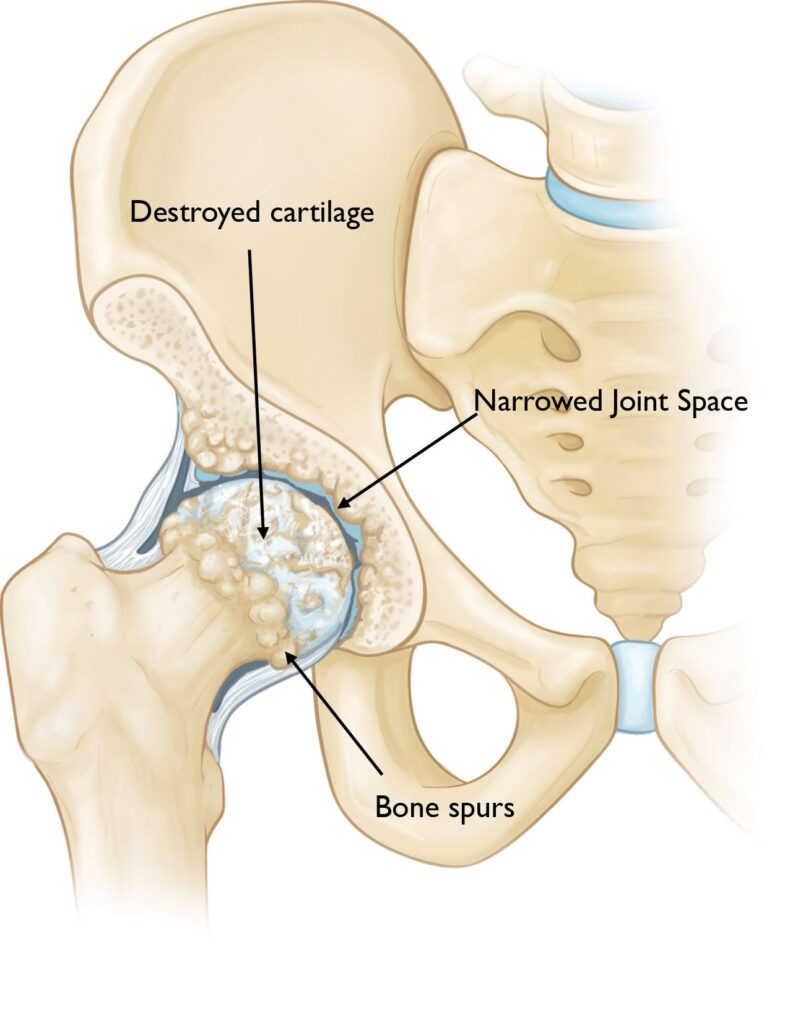
Hip osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease that affects the hip joint, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. At Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre, we specialize in all-encompassing physiotherapy treatments designed to improve our patient’s quality of life by managing and reducing hip OA symptoms.
Causes of Hip Osteoarthritis
Hip OA results from the gradual wear and tear of the cartilage that cushions the hip joint. Several factors contribute to its development:
- Age: As people age, the danger rises.
- Genetics: People may be more susceptible to OA if they have a family history of the disorder. Health
- Joint Injuries: Degeneration of cartilage might be accelerated by prior hip traumas.
- Obesity: Carrying too much weight puts additional strain on the hip joint, accelerating deterioration.
- Structural Abnormalities: OA may result from developmental or congenital conditions that impact hip alignment.
Mechanism of Injury
The cartilage that supports the acetabulum and femoral head gradually deteriorates in hip OA. Bone-on-bone contact brought on by this deterioration results in discomfort and irritation. Osteophytes, or bone spurs, may develop as the disease worsens, further restricting joint motion and making pain worse.
Signs and Symptoms
Common clinical features of hip OA include:
- Pain: Usually in the buttocks, groin, or thigh; becomes better with rest and gets worse with exercise.
- Stiffness: Particularly apparent after periods of inactivity, like waking up in the morning, is stiffness.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Difficulty with hip rotation and bending.
- Crepitus: A grating sensation or sound during hip movements.
- Limping: To minimize pain, individuals may develop an altered gait pattern.
Diagnostic Methods at Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre
At our clinic, we employ a thorough physical and functional assessment to diagnose hip OA:
- Patient History: Talking about the symptoms, when they started, and how they affected day-to-day activities.
- Observation: Evaluating gait, posture, and any obvious abnormalities.
- Palpation: Examining the hip joint for soreness.
- Tests of Range of Motion: Assessing hip suppleness in multiple directions.
- Muscle Strength Tests: Evaluating the hip-supporting muscles’ strength.
- Special Physiotherapy Tests: To diagnose hip OA, we use certain tests:
- Trendelenburg Test: The Trendelenburg Test evaluates the hip abductors’ strength. A positive test result denotes weakness, which is frequently linked to hip OA.
- FABER Test: Identifies problems in the sacroiliac or hip joints. Hip pathology is suggested by pain during this test.
- The Hip Scour Test: Replicates pain through particular movements to identify nonspecific hip pathologies.
- Functional Performance Tests: To evaluate physical function, we use standardized tests.
- The 30-second chair-stand test: Counts the number of stands a patient can complete in 30 seconds to assess lower body strength.
- 40-Meter Fast-Paced Walk Test: Measures walking speed and endurance.
- The Stair-Climb Test: Evaluates functional mobility by measuring the ability to climb and descend stairs.
Physiotherapy Management at Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre
Our approach to managing hip OA is multifaceted, focusing on pain relief, improving joint function, and enhancing overall quality of life:
- Patient education: We discuss hip OA and stress and the value of joint protection techniques and activity adjustment to lessen hip stress.
- Exercise Therapy: Tailored exercise regimens are intended to increase flexibility, balance, and strength in the hip-supporting muscles. These workouts could consist of:
- Exercises for Strengthening: Focusing on the quadriceps, gluteal, and core muscles to support the hip joint.
- Stretching exercises: increasing hip flexor, extensor, and abductors’ range of motion.
- Aerobic Conditioning: Low-impact exercises like swimming or walking that improve cardiovascular health without putting undue strain on the hip joint.
- Manual Therapy: To lessen discomfort and increase joint mobility, our therapists use hands-on methods like soft tissue massage and joint mobilizations.
- High-End Modalities: To improve therapy results, we use cutting-edge therapeutic technology.
- High-Intensity Class IV Laser Therapy: This treatment provides both short-term and long-term pain relief by reducing inflammation and targeting pain receptors.
- Hydrotherapy: Using the buoyancy of water to provide mild workouts that improve strength and flexibility while lowering joint stress.
- Cryotherapy: Using cold therapy to reduce inflammation and numb discomfort to help relieve symptoms.
- Gait Training: To reduce hip strain, we help patients establish the best walking habits possible, with the use of assistive technology if needed.
- Functional Training: By concentrating on everyday tasks, we hope to help patients regain their independence by improving standing, walking, and stair climbing.
Conclusion
With a combination of advanced assessment techniques, targeted exercise programs, manual therapy, and state-of-the-art modalities like high-intensity laser therapy, hydrotherapy, and cryotherapy, our committed team at Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre provides individualized and evidence-based physiotherapy interventions for managing hip osteoarthritis. Our patient-centric approach ensures that each treatment plan is tailored to individual needs, promoting long-term joint health and functional independence. If you or a loved one is experiencing hip osteoarthritis, come to our clinic for professional care and the best physiotherapy solutions available.