Skip to content

Introduction
- Thumb and wrist pain can silently affect daily tasks and sports performance. One common cause is De Quervain’s tenosynovitis. At Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre, we manage this condition with precision and advanced care. Our approach focuses on pain relief, tendon healing, and safe return to activity.
What Is De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis?
- Wrist tendon inflammation is known as De Quervain’s tenosynovitis. The tendons of the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus are involved. These tendons pass through the first dorsal compartment of the wrist. Inflammation makes thumb movements more painful and increases friction.
Causes of De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
- Tendon loading is increased by a number of reasons.
- Repetitive thumb and wrist motions are common reasons.
- Nowadays, the extended use of mobile phones is a significant factor.
- Frequent lifting of infants might also cause problems.
- Risk is increased by manual labor, weight training, and racquet sports.
- Tendon stress is exacerbated by poor wrist biomechanics.
Clinical Features and Symptoms
- Usually, symptoms appear gradually.
- The thumb side of the wrist starts to hurt.
- Gripping or pinching activities exacerbate pain.
- It is possible to see swelling close to the radial styloid.
- Weakness with lifting is a common complaint from patients.
- You can feel crepitus when you move your thumb.
Special Physiotherapy Tests
- Finkelstein’s Test
- The patient clenches their thumb into a fist.
- Gently shift the wrist into ulnar deviation.
- Positivity is indicated by sharp pain across the radial wrist.
- Eichhoff’s Test
- The patient bends the thumb into the palm.
- The examiner deviates the wrist ulnarward.
- Pain reproduction supports the diagnosis.
Physiotherapy Management at Elite Physiotherapy
- Physiotherapy is the gold-standard conservative treatment. We provide individualized, goal-oriented care. Our main goals are to reduce pain, heal tendons, and restore function.
Pain and Inflammation Control
- Thumb spica taping reduces tendon strain.
- Cryotherapy is used for acute pain control.
Advanced Electro-Physical Modalities
Manual Therapy Techniques
- Soft tissue mobilization reduces tendon adhesions.
- Myofascial release improves local circulation.
- Joint mobilization restores wrist biomechanics.
- These techniques reduce mechanical stress on tendons.
Dry Needling and Cupping Therapy
- Dry needling targets myofascial trigger points.
- It reduces muscle overactivity around the wrist.
- Cupping improves blood flow and tissue nutrition.
- Both techniques support faster pain reduction.
Therapeutic Exercise Program
- Exercise forms the core of rehabilitation.
- Isometric thumb exercises begin early.
- Progressive resistance training follows gradually.
- Eccentric loading strengthens tendon fibers.
- Grip strengthening restores hand function.
- Proprioceptive drills improve movement control.
Why Choose Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre?
- We deliver evidence-based physiotherapy care.
- Each program is data-driven and customized.
- Faster recovery is possible by advanced modalities.
- Sports and work-related injuries are among our areas of expertise.
- We prioritize long-term outcomes over short-term respite.
Conclusion
- Expert physiotherapy works well for De Quervain’s tenosynovitis.
- Early management can prevent chronic pain and disability.
- We effectively restore pain-free thumb function at Elite Physiotherapy.
- Make an appointment for your evaluation to advance more quickly and effectively.
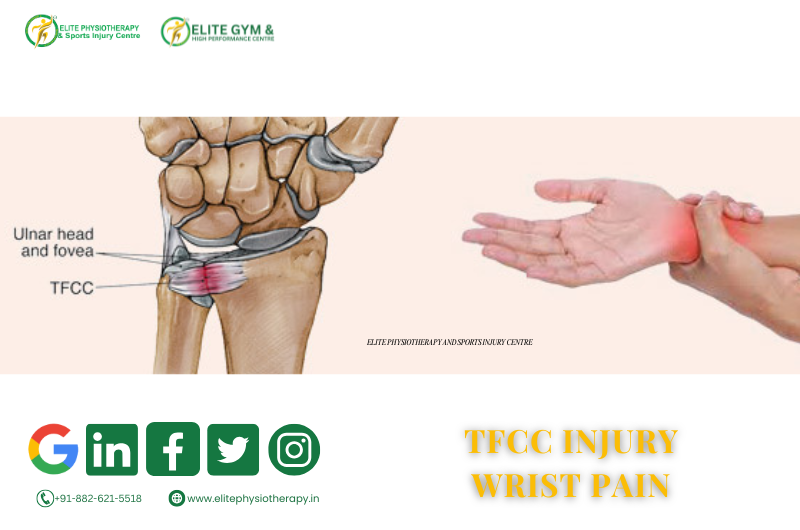
Introduction
- Ulnar-sided (Pinky finger side) wrist pain often limits grip, push, and rotational activities. One common yet overlooked reason is a TFCC injury.
- At Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre, we specialize in precise diagnosis and advanced physiotherapy-led recovery.
What Is the Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC)?
- On the ulnar side of the wrist, the TFCC is a strong fibrocartilaginous structure.
- When the forearm rotates, it keeps the distal radioulnar joint stable.
- Additionally, it relieves pressure between the carpal and ulna bones.
- As a result, it is essential to wrist performance and stability.
Causes of TFCC Injury
- Trauma or degeneration are the causes of TFCC damage.
- A fall on an outstretched hand is one of the common reasons.
- The TFCC can also be harmed by sudden wrist twisting when playing sports.
- Risk is increased by repetitive loading in weightlifting, wrestling, and gymnastics.
- Furthermore, compressive stress is increased by positive ulnar variance.
Types and Classification of TFCC Injuries
- TFCC injuries are broadly classified into two groups.
- Traumatic TFCC Tears
- These result from acute injury.
- They are common in athletes and active individuals.
- Degenerative TFCC Tears
- These develop gradually with age or repetitive stress.
They are common in manual workers and veteran athletes.
Clinical Features and Symptoms
- Patients typically complain of ulnar wrist pain.
- When squeezing or rotating the forearm, pain intensifies.
- It’s typical to report clicking or catching feelings.
- Reduced load tolerance and wrist weakness are common symptoms.
- In acute situations, there may be swelling.
Special Physiotherapy Tests for diagnosis
- TFCC Compression Test:
- Ulnar deviation with axial loading reproduces deep ulnar wrist pain.
- Supination Lift Test:
- Pain occurs when lifting against resistance with supinated forearm.
- Press Test:
- Pain appears while pushing up from a seated position.
- Positive findings guide targeted physiotherapy planning.
Physiotherapy Management of TFCC Injury
- Physiotherapy is the cornerstone of conservative TFCC management.
- Our approach is personalized, progressive, and evidence-based.
Phase 1: Pain and Inflammation Control
- Our first goal is to lessen pain and swelling.
- The healing TFCC is protected by activity modulation.
- External support is provided by wrist bracing or tape.
- High Intensity Laser Therapy accelerates tissue healing.
- It reduces inflammation and improves microcirculation.
- Super Inductive System (SIS) decreases pain and muscle guarding.
- It also improves neuromuscular activation safely.
Phase 2: Mobility and Stability Restoration
- Controlled mobility starts as soon as the discomfort subsides.
- We progressively regain range of motion in the wrist and forearm.
- Painless movements are emphasized.
- Exercises for stabilizing the distal radioulnar joint are presented.
- Joint awareness and control are enhanced by proprioceptive training.
Phase 3: Strengthening and Load Progression
- Strengthening focuses on forearm rotators and wrist stabilizers.
- Eccentric and isometric exercises are carefully progressed.
- Grip endurance training restores functional capacity.
- Shock Wave Therapy may be used in chronic degenerative cases.
- It stimulates tissue regeneration and pain modulation.
Phase 4: Advanced Modalities and Soft Tissue Care
- Dry Needling reduces myofascial tightness around the wrist and forearm.
- It improves movement efficiency and pain tolerance.
- Cupping Therapy enhances local blood flow and fascial mobility.
- It supports recovery in chronic and overuse presentations.
Phase 5: Return to Sport and Prevention
- Sport-specific drills are gradually introduced.
- Load management strategies reduce reinjury risk.
- Technique correction improves long-term wrist health.
- Return-to-sport decisions are criteria-based, not time-based.
Why choose Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre for TFCC injury?
- We combine advanced technology with expert clinical reasoning.
- Each TFCC case receives individualized attention.
- Our focus remains on complete recovery and performance optimization.
- We treat athletes, professionals, and active individuals alike.
Conclusion
- TFCC injuries demand early diagnosis and expert physiotherapy care.
- Ignoring symptoms can lead to chronic wrist instability.
- With advanced modalities and structured rehabilitation, recovery is achievable.


